St. Britto Hr. Sec. School - Madurai
12th Physics Monthly Test - 3 ( Current Electricity )-Aug 2020
-
-
-
-
Define electrical resistivity
-
Why current is a scalar?
-
why is terminal voltage of a cell less than its emf?
-
Define resistance
-
Draw I - V graph for a conductor. What does the slope represent?
-
What is (i) thermoelectric current
(Ii) thermocouple. -
Distinguish between drift velocity and mobility.
-
-
When resistors are connected in series. the effective resistance is increased. Why?
-
State Kirchhoff’s voltage rule.
-
-
What is Peltier effect?
-
What is Seebeck effect?
-
Why the resistance of the conductor increases with rise in temperature.
-
What is Seebeck effect?
-
Obtain the condition for bridge balance in Wheatstone’s bridge.
-
In a circuit containing internal resistance r. Find the power delivered
-
Calculate the equivalent resistance between A and B in the given circuit.
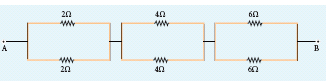
-
-
Determine the number of electrons flowing per second through a conductor, when a current of 32 A flows through it.
-
Derive an expression of drift velocity and write the relation between drift velocity and mobility.
-
-
A potential difference across 24 Ω resistor is 12 V. What is the current through the resistor?
-
Explain Peltier effect.
-
A copper wire of cross-sectional area 0.5 mm2 carries a current of 0.2 A. If the free electron density of copper is 8.4 × 1028 m-3 then compute the drift velocity of free electrons.
-
Obtain the macroscopic form of Ohm’s law from its microscopic form and discuss its limitation.
-
What are carbon resistors? What does the colour indicates?
-
The resistance of a wire is 20 Ω. What will be new resistance, if it is stretched uniformly 8 times its original length?
-
Two metallic wires PI &P2 of the same material & same length but different cross sectional areas Al & A2 are joined together & connected to a source of emf. Find the ratio of the drift velocities of free electrons in the two wires when they are connected (i) in series & (ii) in parallel.
-
-
Obtain the condition for bridge balance in Wheatstone's bridge.
-
Write mathematical relation between mobility & drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor (ii) mobility & relaxation time (or) mean free time.
-
-
A copper wire of 10-6 m2 area of cross section, carries a current of 2 A. If the number of electrons per cubic meter is 8 × 1028, calculate the current density and average drift velocity.
-
What is potentiometer? Give its constant and principle.
-
Two cells each of 5V are connected in series across a 8 Ω resistor and three parallel resistors of 4 Ω, 6 Ω and 12 Ω. Draw a circuit diagram for the above arrangement. Calculate i) the current drawn from the cell (ii) current through each resistor
-
An electronics hobbyist is building a radio which requires 150 Ω in her circuit, but she has only 220 Ω, 79 Ω and 92 Ω resistors available. How can she connect the available resistors to get desired value of resistance?
-
Two students A & B were asked to pick a resistor of 25 k from a collection of carbon resistors. A picked a resistors with bands of colours of red, green, orange, white. B picked a resistor with bands of colours: black, green, red who picked the correct resistor?
-
Obtain an expression for electrical conductor
