St. Britto Hr. Sec. School - Madurai
12th Physics Monthly Test - 1( Current Electricity)-Aug 2020
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The electrical resistivity drops to zero for__________
conductors
insulators
super conductors
semiconductors
-
The unit of temperature coefficient of resistance is_______.
°C
°C-1
-C-2
°C2
-
A wire connected to a power supply of 230 V has power dissipation P1. Suppose the wire is cut into two equal pieces and connected parallel to the same power supply. In this case power dissipation is P2. The ratio \(\frac{P_2}{P_1}\) is
1
2
3
4
-
-
What is seeback effect?
-
What is conductor?
-
-
Derive the expression for power P=VI in electrical circuit.
-
Why the resistance of the conductor increases with rise in temperature.
-
Define resistance
-
The resistivity of materials depends upon what parameters?
-
What is superconductivity?
-
State microscopic form of Ohm’s law.
-
What is Thomson effect?
-
What is meant by Heating effect of electric current?
-
-
When resistors are connected in series. the effective resistance is increased. Why?
-
why is terminal voltage of a cell less than its emf?
-
-
When resistors are connected in parallel the effectiveresistance is reduced. Why
-
Draw V - I graph for ohmic & non -ohmic materials. give example
-
What is the effective resistance of resistors connected in series
-
State macroscopic form of Ohm’s law.
-
Two wires A & B are of the same metal of of same length have area of cross section in the
ratio of 2 : If the same potential difference is applied across each wire. What will be the retro of the circuit flowing in A & B? -
-
How does one can understand the temperature dependence of resistivity of a conductor?
-
Calculate the equivalent resistance for the circuit which is connected to 24 V battery and also find the potential difference across 4 Ω and 6 Ω resistors in the circuit.
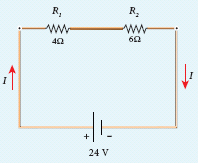
-
-
The resistance of a wire is 20 Ω. What will be new resistance, if it is stretched uniformly 8 times its original length?
-
Derive an expression of drift velocity and write the relation between drift velocity and mobility.
-
Calculate the equivalent resistance in the following circuit and also find the current I, I1 and I2 in the given circuit.

-
What are carbon resistors? What does the colour indicates?
-
Compute the current in the wire if a charge of 120 C is flowing through a copper wire in 1 minute.
-
Resistance of a material at 100C and 400C are 45 Ω and 85 Ω respectively. Find its temperature co-efficient of resistance.
-
Explain Peltier effect.
-
Find the expression for the equivalent emf & internal resistance of the series combination of cells
-
-
If the resistance of coil is 3 Ω at 20oC and α = 0.004/oC then determine its resistance at 100oC.
-
In a circuit containing internal resistance r. Find the power delivered
-
-
From the given circuit,
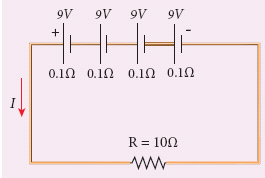
Find
i) Equivalent emf of the combination
ii) Equivalent internal resistance
iii) Total current
iv) Potential difference across external resistance
v) Potential difference across each cell -
How will you represent a resistor of 3700\(\Omega \) ± 10 by colour code?
-
Write mathematical relation between mobility & drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor (ii) mobility & relaxation time (or) mean free time.
-
-
How the emf of two cells are compared using potentiometer?
-
A cell supplies a current of 0.9 A through a 2 Ω resistor and a current of 0.3 A through a 7 Ω resistor. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell.
-
-
The resistance of a nichrome wire at 0 0C is 10 Ω. If its temperature coefficient of resistance is 0.004/0C, find its resistance at boiling point of water. Comment on the result.
