MABS Institution
11th Physics Monthly Test - 1 ( Heat and Thermodynamics )-Aug 2020
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Give an equation state for an isochoric process.
-
Obtain an ideal gas law from Boyle’s and Charles’ law.
-
What is meant by Convection?
-
What is a principle of calorimetry?
-
Applying first law of thermodynamics, write relation between P & T.
-
Write the important properties of thermal radiations.
-
A steam engine boiler is maintained at 250°C and water is converted into steam. This steam is used to do work and heat is ejected to the surrounding air at temperature 300K. Calculate the maximum efficiency it can have?
-
Calculate the heat required to convert 0.6 kg of ice at - 20°C, kept in a calorimeter to steam at 100°C atmospheric pressure, Given the specific heat capacity (Lice) of lee= 2100 Jkg-1K-1.
-
Refrigerator is to maintain eatables kept inside at 9°C. If room temperature is 36°C. Calculate the co efficient of performance.
-
How does the density of a solid or a liquid vary with temperature? State that its variation with temperature is given by P' = P(1 -\(\alpha\)\(\triangle\)T), where y is coefficient of cubical expansion.
-
-
2 kg of ice at -20°C is mixed with 5 kg of water at 20°C in an insulating vessel having a negligible heat capacity. Calculate the final mass of water remaining in the container.
-
Derive the equation of state \({ Tv }^{ \gamma -1 }\) = constant.
-
-
A 0.5 mole of gas at temperature 300 K expands isothermally from an initial volume of 2 L to 6 L
(a) What is the work done by the gas?
(b) Estimate the heat added to the gas?
(c) What is the final pressure of the gas?
(The value of gas constant, R = 8.31 J mol-1 K-1) -
How does the internal energy of a thermodynamic system change?
-
One mole of an ideal gas initially kept in a cylinder at pressure 1 MPa and temperature 27°C is made to expand until its volume is doubled.
(a) How much work is done if the expansion is (i) adiabatic (ii) isobaric (iii) isothermal?
(b) Identify the processes in which change in internal energy is least and is maximum.
(c) Show each process on a PV diagram.
(d) Name the processes in which the heat transfer is maximum and minimum.
(Take \(\Upsilon =\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \) and R=8.3 J mol-1 K-1) -
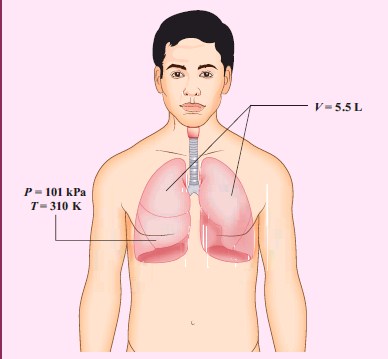
When a person breaths, his lungs can hold up to 5.5 Litre of air at body temperature 37°C and atmospheric pressure (1 atm =101 kPa). This Air contains 21% oxygen. Calculate the number of oxygen molecules in the lungs.
-
Distinguish between isothermal and adiabatlc process.
-
What is meant by coefficient of linear expansion superficial & cubical expansion?
-
Explain in detail Newton’s law of cooling.
-
Explain the meaning of heat and work with suitable examples.
-
-
Explain Wien’s law and why our eyes are sensitive only to visible rays?
-
Estimate the mass of air in your class room at NTP. Here NTP implies normal temperature (room temperature) and 1 atmospheric pressure

-
-
Give some examples of irreversible processes.
-
Describe the anomalous expansion of water. How is it helpful in our lives?
