MABS Institution
11th Chemistry Monthly Test - 1 ( Gaseous State )-Aug 2020
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
What are isobar and isochores?
-
Distinguish between diffusion and effusion.
-
State Dalton's law of partial pressure.
-
Under what conditions, do real gases behave ideally?
-
Explain Joule Thomson effect.
-
A small bubble rises from the bottom of a lake where the temperature and pressure are 8°C and 6.4 atm. to the water surface, where the temperature is 25°C and pressure is 1atm. Calculate the final volume in (mL) of the bubble, if its initial volume is 2.1 mL.
-
Explain the graphical representation of Avogadro's hypothesis.
-
A mixture of gases contains 4.76 mole of Ne, 0.74 mole of Ar and 2.5 mole of Xe. Calculate the partial pressure of gases, if the total pressure is 2 atm. at a fixed temperature. Solve this problem using Dalton's law.
-
A sample of gas has a volume of 8.5 dm3 at an unknown temperature. When the sample is submerged in ice water at 0 °C, its volume gets reduced to 6.37 dm3. What is its initial temperature?
-
-
In the below figure, let us find the missing parameters [volume in (b) and pressure in (c)]
P1 = 1 atm, P2 = 2 atm, P3 = ? atm
V1 = 1dm3, V2 =? dm3, V3 = 0.25 dm3
T1 = 298 K, T2 = 298 K, T3 = 298 K.
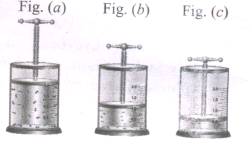
-
Sulphur hexafluoride is a colouriess, odourless gas; calculate the pressure exerted by 1.82 moles of the gas in a steel vessel of volume 5.43 dm3 at 69.5°C, assuming ideal gas behaviour.
-
-
Explain the graphical representation of Boyle's law.
-
Derive ideal gas equation.
-
Argon is an inert gas used in light bulbs to retard the vaporization of the tungsten filament. A certain light bulb containing argon at 1.2 atm and 18°C is heated to 85°C at constant volume. Calculate its final pressure in atm.
-
What is compressibility factor? How does it explain the deviation of non ideal gases from ideal behaviour.
-
Vanderwaal's constant for a gas (g) are a = 6.34 atm lit-2; and b = 52.6 ml mol-1. Find the critical temperature and critical pressure of the gas.
-
A flammable hydrocarbon gas of particular volume is found to diffuse through a small hole in 1.5 minutes. Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure an equal volume of bromine vapour takes 4.73 min to diffuse through the same hole. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas and suggest what this gas might be, (Given that molar mass of bromine = 159.8 g/mole
-
An athlete in a kinesiology research study has his lung volume of 7.05 dm3 during a deep inhalation. At this volume, the lungs contain 0.312 mole of air. During exhalation, the volume of his lung decreases to 2.35 dm3. How many moles of air does the athlete exhale during exhalation? (assume pressure and temperature remain constant).
-
Explain the following observations
(a) Aerated water bottles are kept under water during summer
(b) Liquid ammonia bottle is cooled before -opening the seal
(c) The tyre of an automobile is inflated to slightly lesser pressure in summer than in winter
(d) The size of a weather balloon becomes larger and larger as it ascends up into larger altitude -
Vanderwaal's constant for gas are a = 3.67 atm lit2 mol-2 b = 0.0408 lit mol-1. Find the critical temperature and critical pressure of the gas.
-
How will you calculate the partial pressure in terms of mole fraction?
-
-
Explain Andrew's isotherm of carbon dioxide.
-
Describe an experiment to verify Boyle's law.
-
-
At 27°C temperature and 4 bar pressure CO is filled in 2 litre vessel. Find the pressure if it is filled in 4 litre vessel at 77 °C temperature.
-
Find the moles of O2 gas having pressure 250 bar in 500 ml vessel at 350 k temperature.
