MABS Institution
11th Chemistry Monthly Test - 1 ( Basic concept of organic reactions )-Aug 2020
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
How will substitution reactions die classified?
-
Predict the product for the following reaction.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
-
How will you distinguish between electrophiles and nucleophiles?
-
Mention the types of fission of a covalent bond?
-
Which of the following ions is more stable? Use resonance to explain your answer.
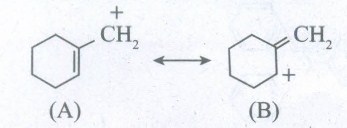
-
Which bond is more polar in the following pair of molecular?
(i) H3C-H (or) H3C-Br
(ii) H3C-NH2 (or) H3C-OH
(iii) H3C-OH (or) H3C-SH -
What are the possible types of electron movement? Represent them by clearly indicating the electron shift.
-
Distinguish between electrophiles and nucleophiles
-
Explain the substitution reaction in detail with suitable examples.
-
Discuss the reason behind the classification of inductive effect into +I and -I effect.
-
-
Carry over the following reaction mechanisms.
(i) Bromination of alkene
(ii) Addition of HCN to CH3CHO
(iii) Formation of alkyl bromide with benzoyl peroxide as radical initiator. -
Write structures of various carbocations that can be obtained from 2-methyl butane. Arrange these carbocations in order of increasing stability.
-
-
Which of the following compounds will not exist as resonance hybrid? Give reason for your answer.
(i) CH3 - OH
(ii) R-CONH2
(iii) CH3-CH = CH-CH2NH2 -
While writing the resonance structures, what are the rules to be followed?
-
The structure of triphenylmethyl cation is given below. This very stable and some of its salts can be stored for months. Explain the cause of high stability of this cation.
-
Explain the types of addition reactions?
-
Give a detailed account on homolytic and heterolytic cleavage.
-
How does hyper conjugation effect explain the stability of alkenes?
-
Explain the types of substitution reaction?
-
Explain the acidic nature of phenol.
-
An organic compound (A) has a molecular formula C2H60 it is one of the primary alcohol. A reacts with acidified potassium dichromate to give B. B on further undergoes to oxidation reaction to give C. C on reacts with SOCl2 to give D which is chlorinated product. Identify A,B,C and D, explain with equation.
-
Complete the reactions and identify the products.
(i)
(ii)
\({ CH }_{ 3 }-\underset { \overset { | }{ Cl } }{ C } H-{ CH }_{ 3 }\overset { { H }^{ + }/{ K }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 } }{ \longrightarrow } A\overset { (O)) }{ \longrightarrow } B\) -
-
An organic compound (A) of a molecular formula C2H4 which is a simple alkene. A reacts with dil H2SO4 to give B. A again reacts with Cl2 to give C. Identify A,B and C and write the equations.
-
How does inductive effect influence the reactivity and acidity of carboxylic acids?
-
-
Explain electron movement in organic reactions.
